ABRASION - The destruction of a material caused by scraping or rubbing against a rough, hard surface.
ABRASION MACHINE - A laboratory device for determining the abrasion resistance of wire and cable. The two standard types of machines are the squirrel cage, with square steel bars, and the abrasive grit type.
ABRASION RESISTANCE - The ability of a wire or cable jacket to resist surface wear.
AC - Abbreviation for alternating current. See alternating current. Also abbreviated as ac.
ACCELERATED LIFE TEST - A test in which a cable is subjected to extreme conditions to determine the life of a cable.
ACCELERATOR - Chemical additive which hastensa chemical reaction, e.g., a compound added to rubber or Neoprene® mixtures to reduce curing time. Neoprene® is a trademark of the DuPont de Nemours Co.
ACR - Designation for cable with corona resisting insulation.
ACRS - Aluminum conductor, steel reinforced. Aluminum wires stranded around a steel core. Usually used for high voltage cross-country transmission lines.
ADAPTER - a) Device used for joining two fiber optic connectors together. b) A device for connecting two parts (of different diameters) of an apparatus.
ADHESIESIESIVE - Usually a synthetic material which, when applied to tapes, potting operations, etc., permits materials to be bonded together.
ADMITTANCE - Symbol
Y. The reciprocal of impedance.Given by the formula:
Y = G + iB
where
G is the conductance,
B the susceptance, and
i equals
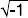
. Since impedance,
Z, is given by:
Z = R + iX
AEC - Atomic Energy Commission. The government agency which oversees all atomic energy projects.